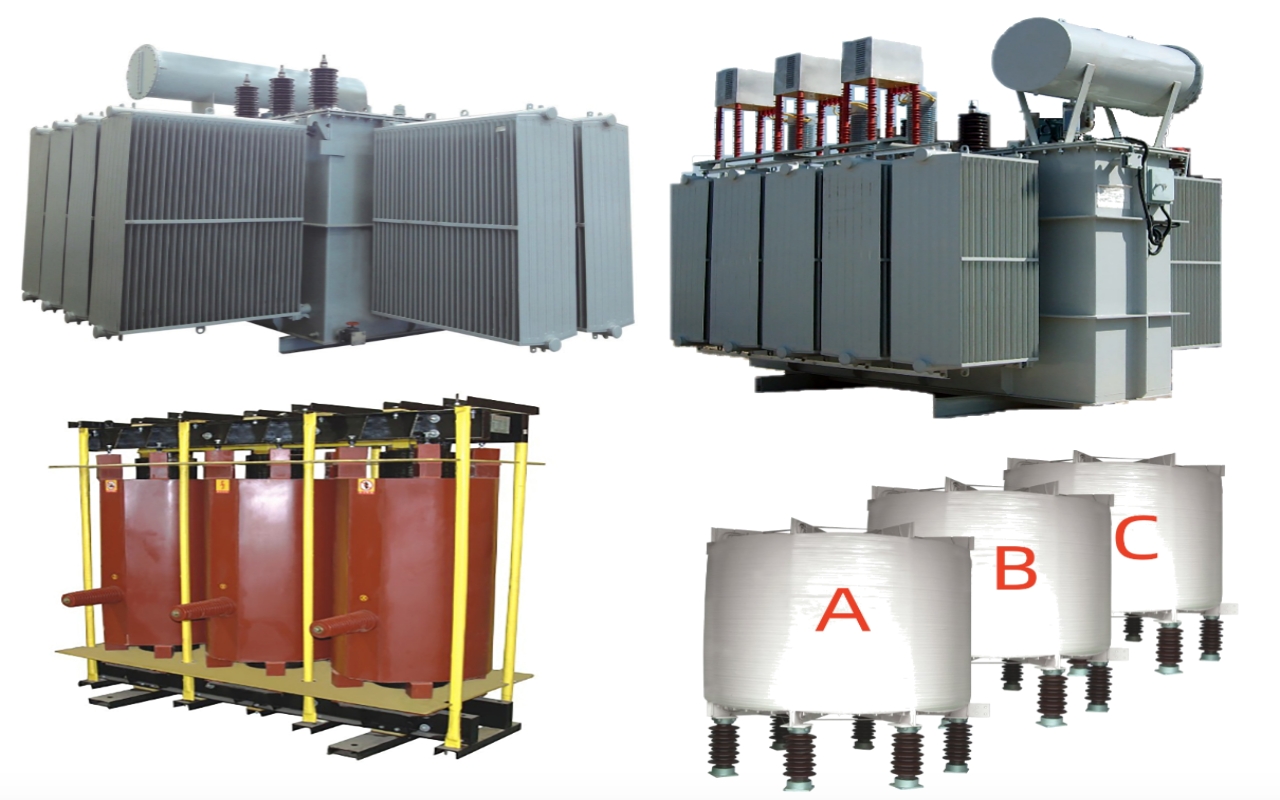
0102030405
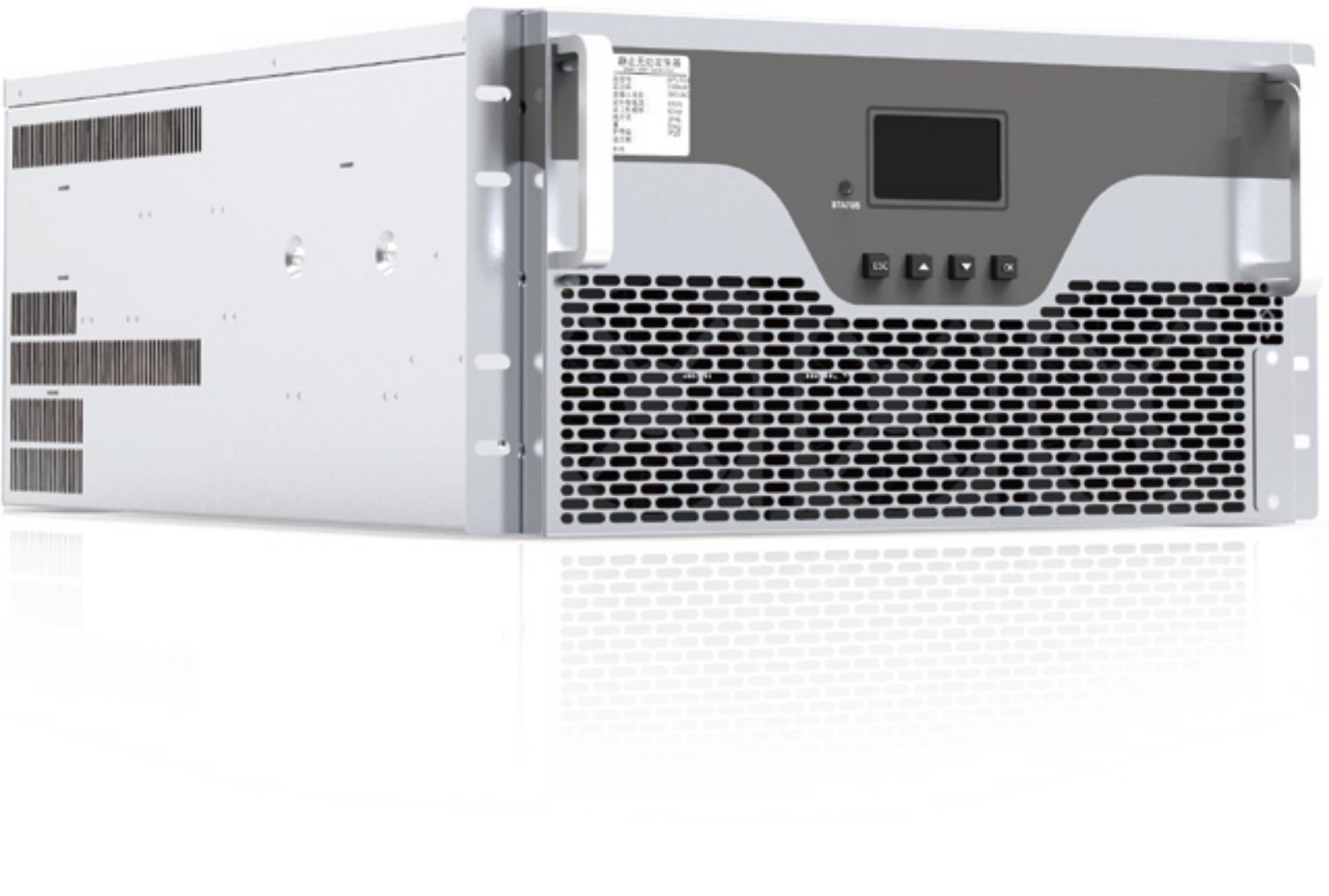
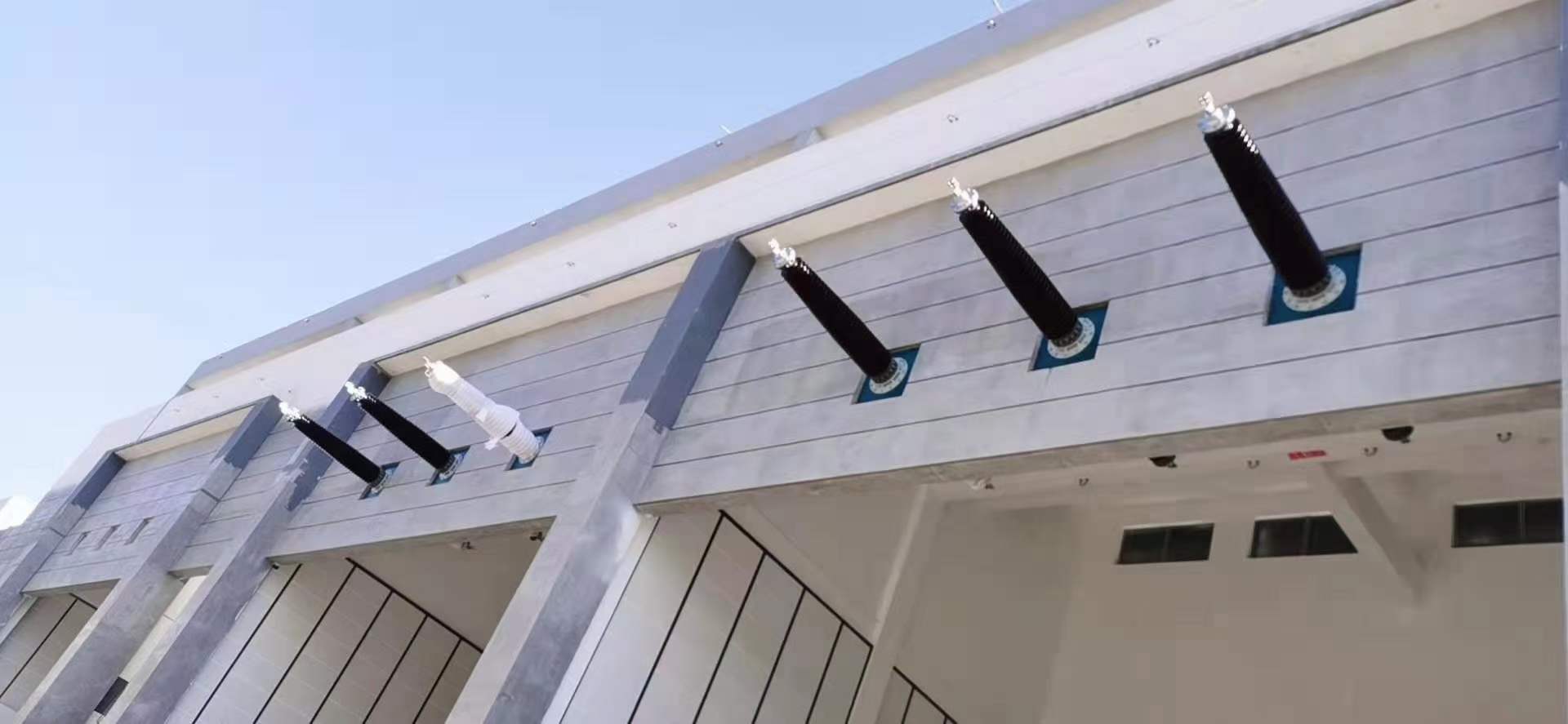
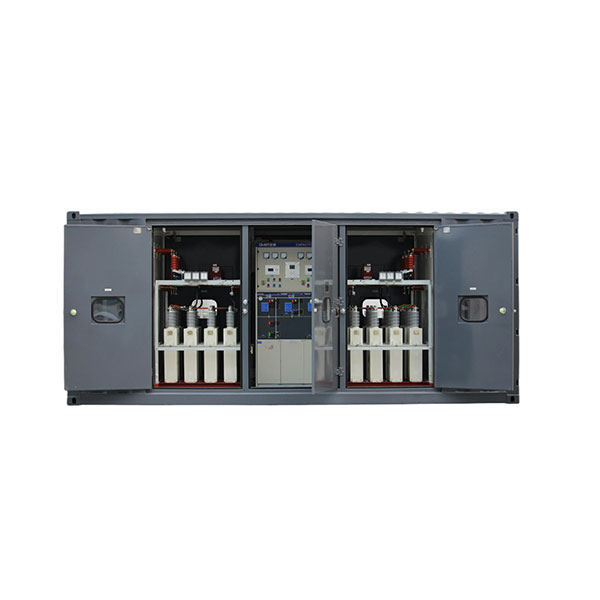
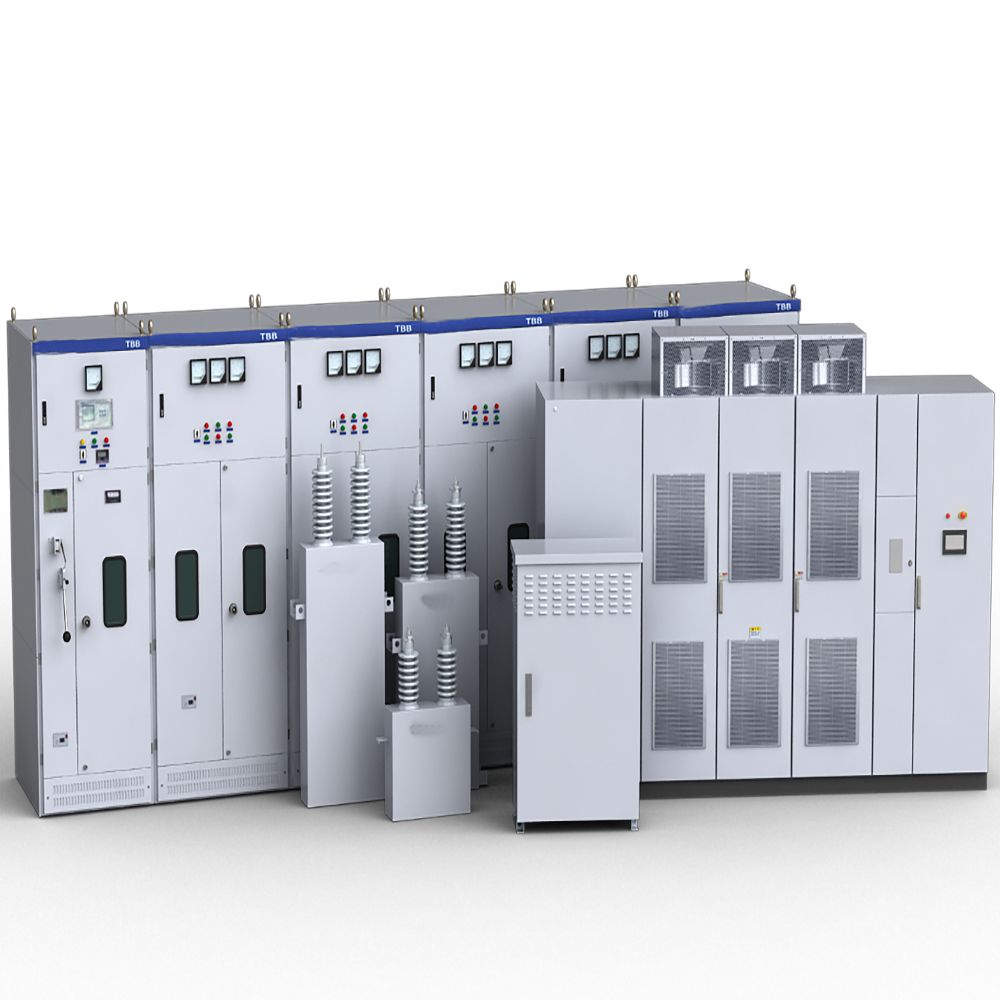
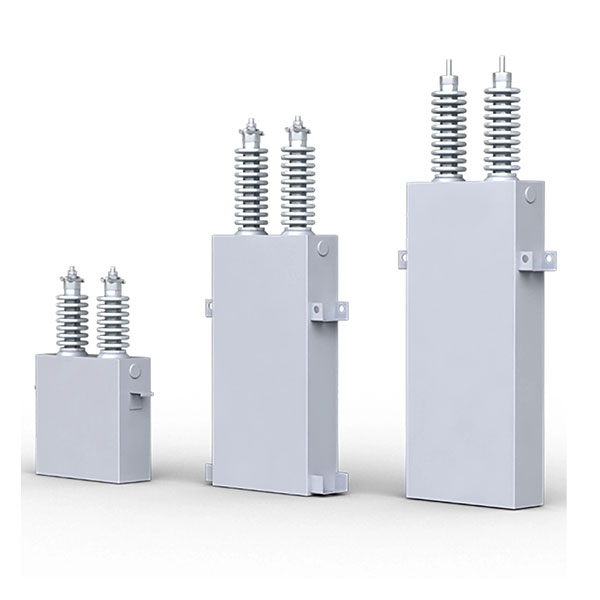
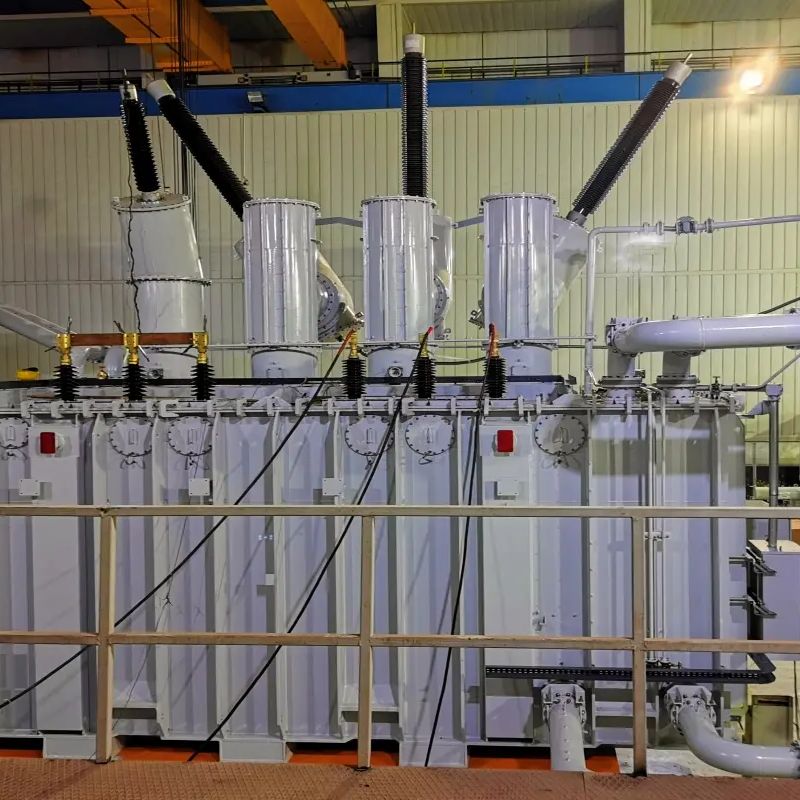
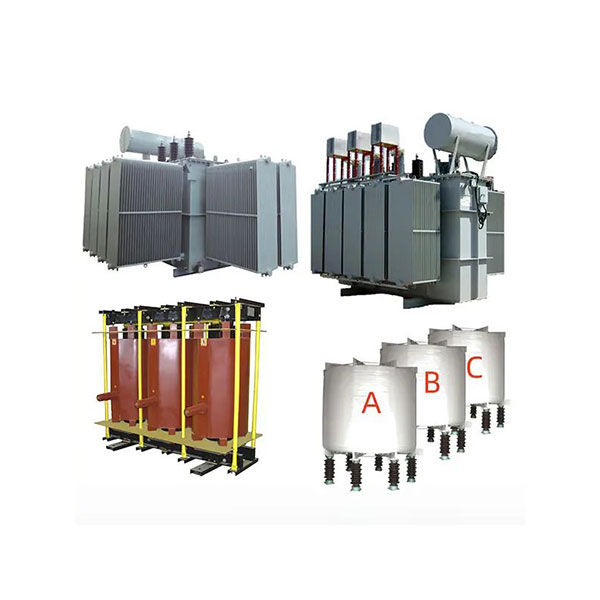
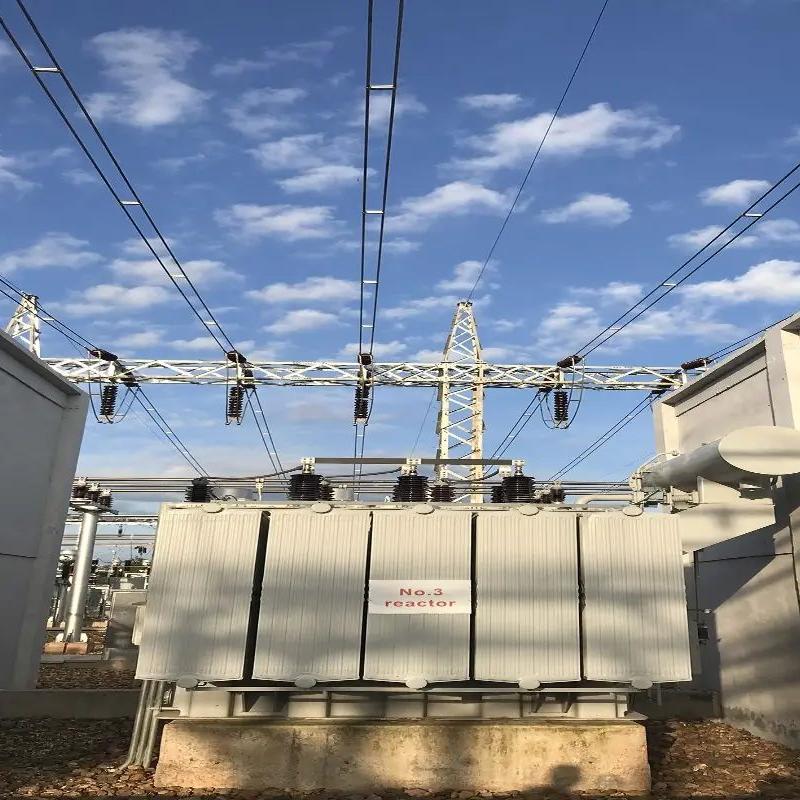
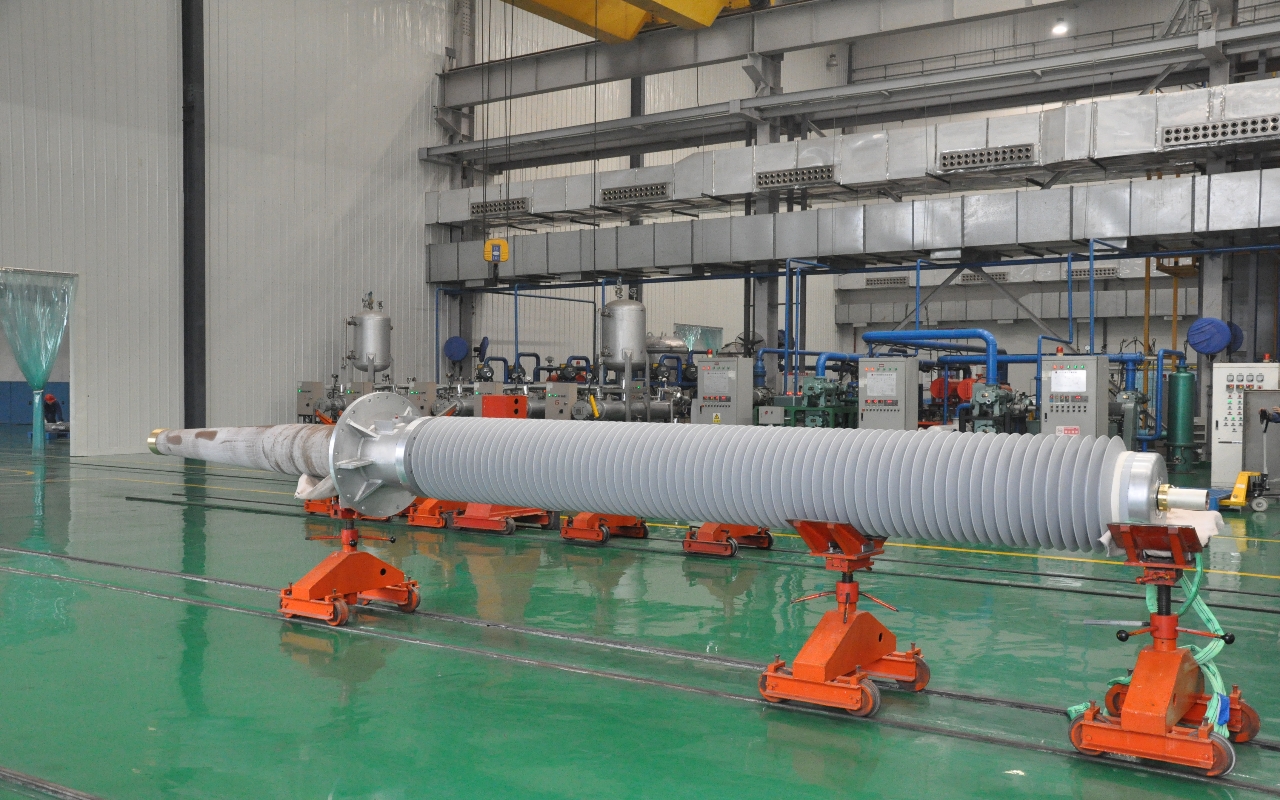
6-220kV high voltage Reactor
Reactors
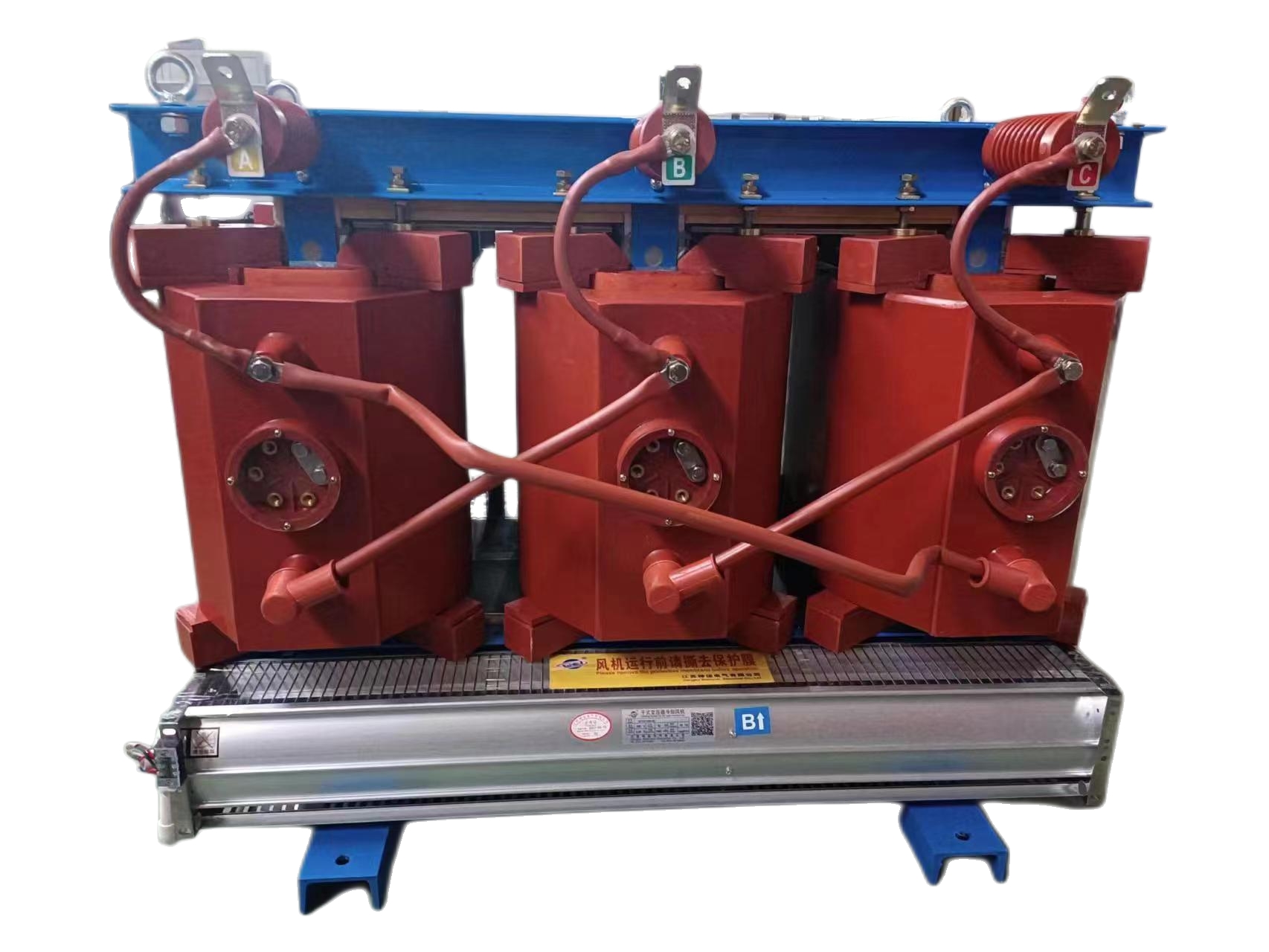
Reactors, also known as inductors, are widely used in circuits. Due to the electromagnetic induction effect, there is a certain degree of inductance in the circuit, which can prevent current changes. When a conductor is energized, a magnetic field is generated within a certain range of space it occupies, so all current carrying electrical conductors have a general sense of inductance. However, the inductance of a long and straight conductor is relatively small, and the magnetic field generated is not strong. Therefore, the actual reactor is a wire wound in the form of a solenoid, called a hollow reactor;
Sometimes, in order to increase the inductance of this solenoid, an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, which is called an iron core reactor. Reactance is divided into inductive reactance and capacitive reactance. A more scientific classification is that inductive reactance (inductor) and capacitive reactance (capacitor) are collectively referred to as reactors. However, due to the existence of inductors in the past, which were called reactors, capacitors are now referred to as capacitive reactances, and reactors specifically refer to inductors.
 The commonly used reactors in power systems include series reactors and parallel reactors. Series reactors are mainly used to limit short-circuit currents, and can also be connected in series or parallel with capacitors in filters to limit high-order harmonics in the power grid. Reactors in 220kV, 110kV, 35kV, and 10kV power grids are used to absorb capacitive reactive power from cable lines during charging. The operating voltage can be adjusted by adjusting the number of parallel reactors. Ultra high voltage parallel reactors have various functions to improve the operating conditions related to reactive power in power systems, mainly including:
1. The capacitance effect on lightly unloaded or lightly loaded lines to reduce transient overvoltage at power frequency;
2. Improve voltage distribution on long-distance transmission lines;
3. To balance the reactive power in the line as much as possible on site during light loads, preventing unreasonable flow of reactive power and reducing power loss on the line;
4. Reduce the steady-state voltage of the power frequency on the high-voltage bus when the large unit is parallel to the system, making it easier for the generator to be synchronized and parallel;
5. Prevent self excitation resonance phenomenon that may occur in generators with long lines;
6. When using a reactor neutral point through a small reactance grounding device, a small reactor can also be used to compensate for the phase to phase and phase to ground capacitance of the line, in order to accelerate the automatic extinguishing of the latent current and facilitate its use.
The wiring of reactors can be divided into two ways: series connection and parallel connection. Series reactors usually serve as current limiting devices, while parallel reactors are often used for reactive power compensation.
The commonly used reactors in power systems include series reactors and parallel reactors. Series reactors are mainly used to limit short-circuit currents, and can also be connected in series or parallel with capacitors in filters to limit high-order harmonics in the power grid. Reactors in 220kV, 110kV, 35kV, and 10kV power grids are used to absorb capacitive reactive power from cable lines during charging. The operating voltage can be adjusted by adjusting the number of parallel reactors. Ultra high voltage parallel reactors have various functions to improve the operating conditions related to reactive power in power systems, mainly including:
1. The capacitance effect on lightly unloaded or lightly loaded lines to reduce transient overvoltage at power frequency;
2. Improve voltage distribution on long-distance transmission lines;
3. To balance the reactive power in the line as much as possible on site during light loads, preventing unreasonable flow of reactive power and reducing power loss on the line;
4. Reduce the steady-state voltage of the power frequency on the high-voltage bus when the large unit is parallel to the system, making it easier for the generator to be synchronized and parallel;
5. Prevent self excitation resonance phenomenon that may occur in generators with long lines;
6. When using a reactor neutral point through a small reactance grounding device, a small reactor can also be used to compensate for the phase to phase and phase to ground capacitance of the line, in order to accelerate the automatic extinguishing of the latent current and facilitate its use.
The wiring of reactors can be divided into two ways: series connection and parallel connection. Series reactors usually serve as current limiting devices, while parallel reactors are often used for reactive power compensation.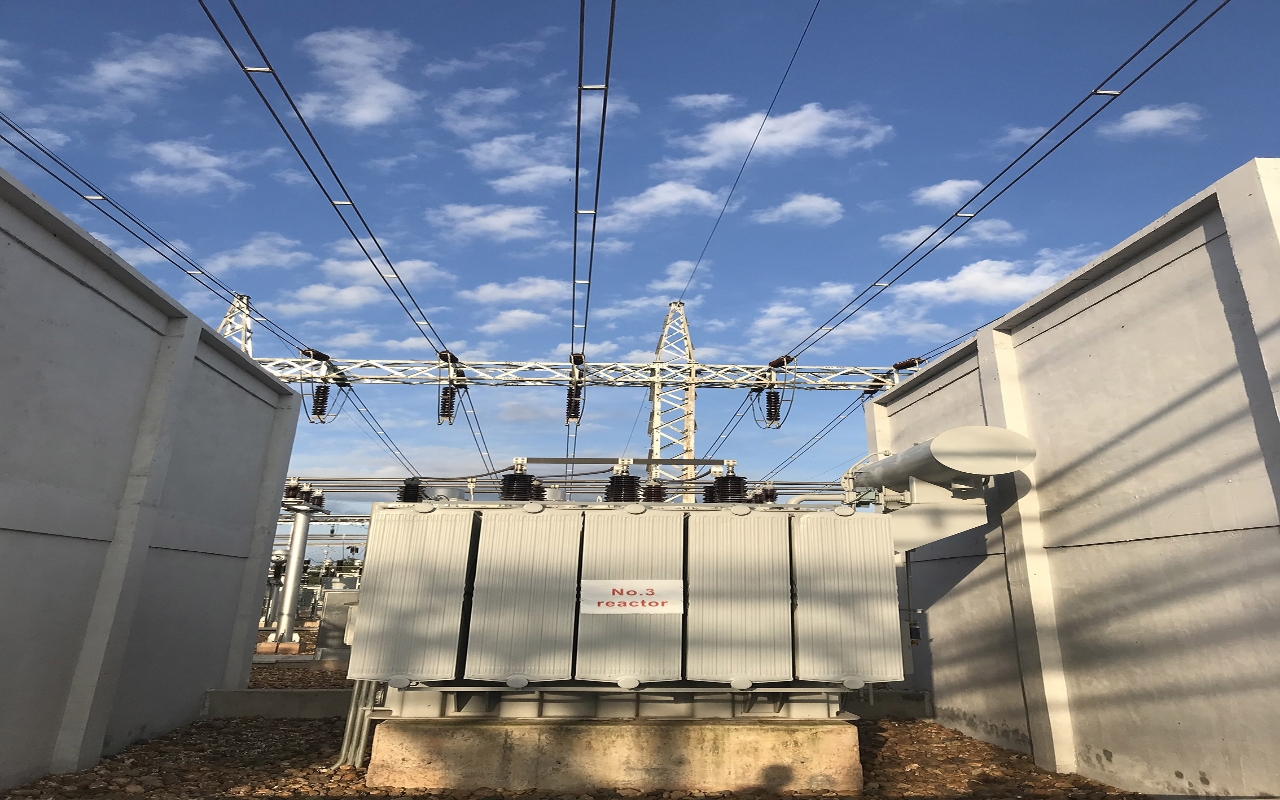
description2
description2