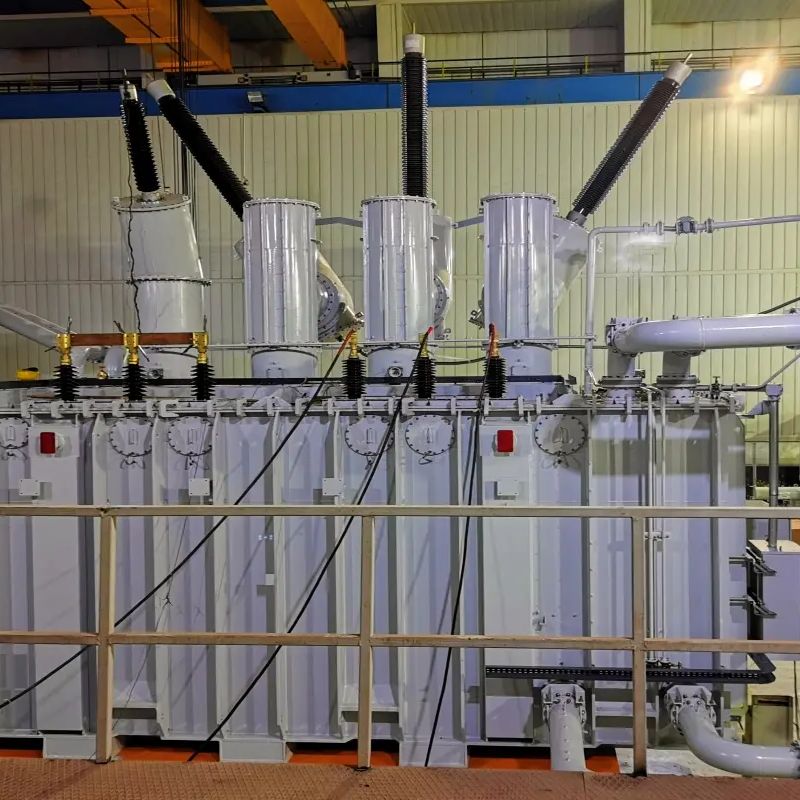
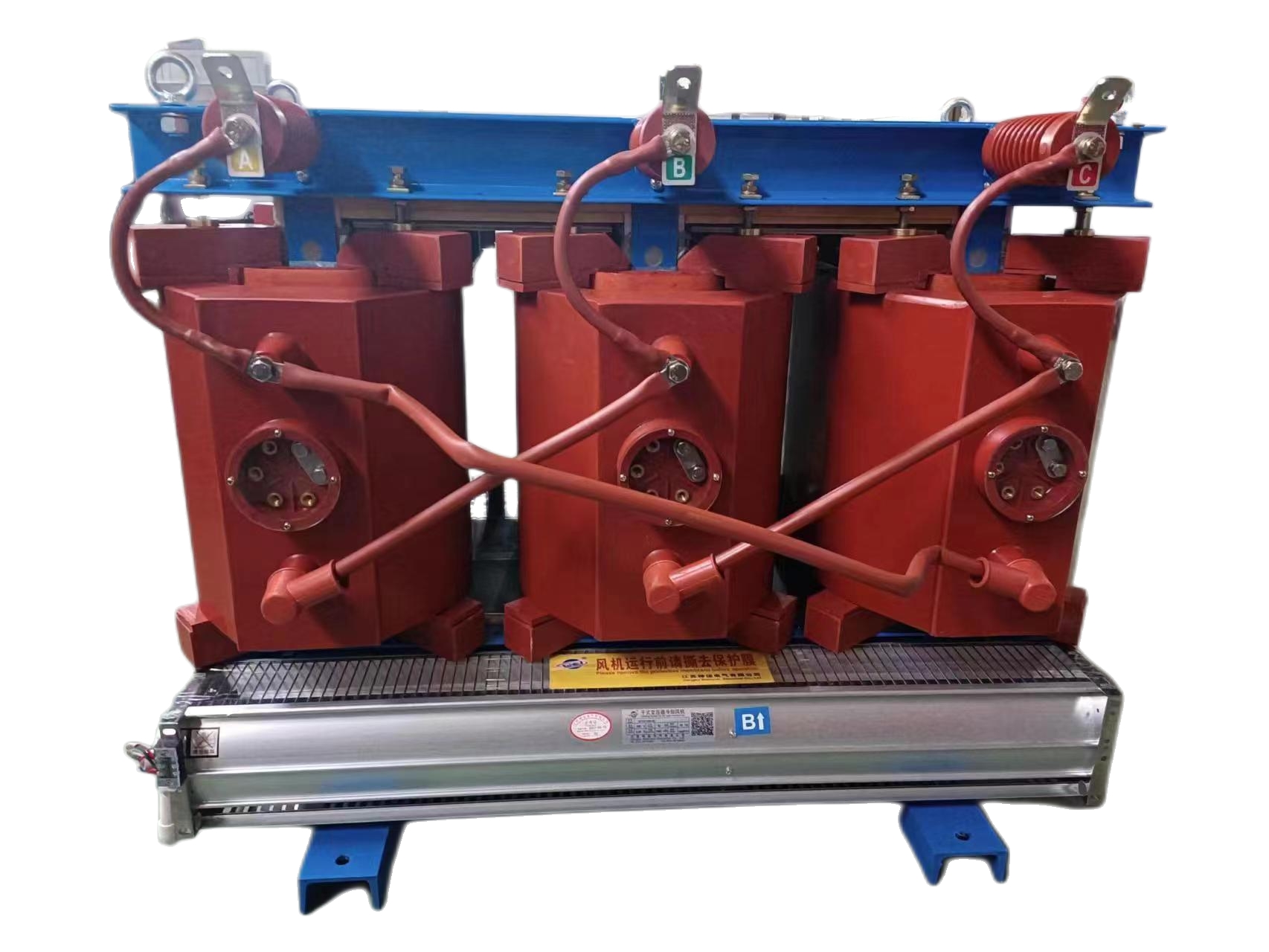
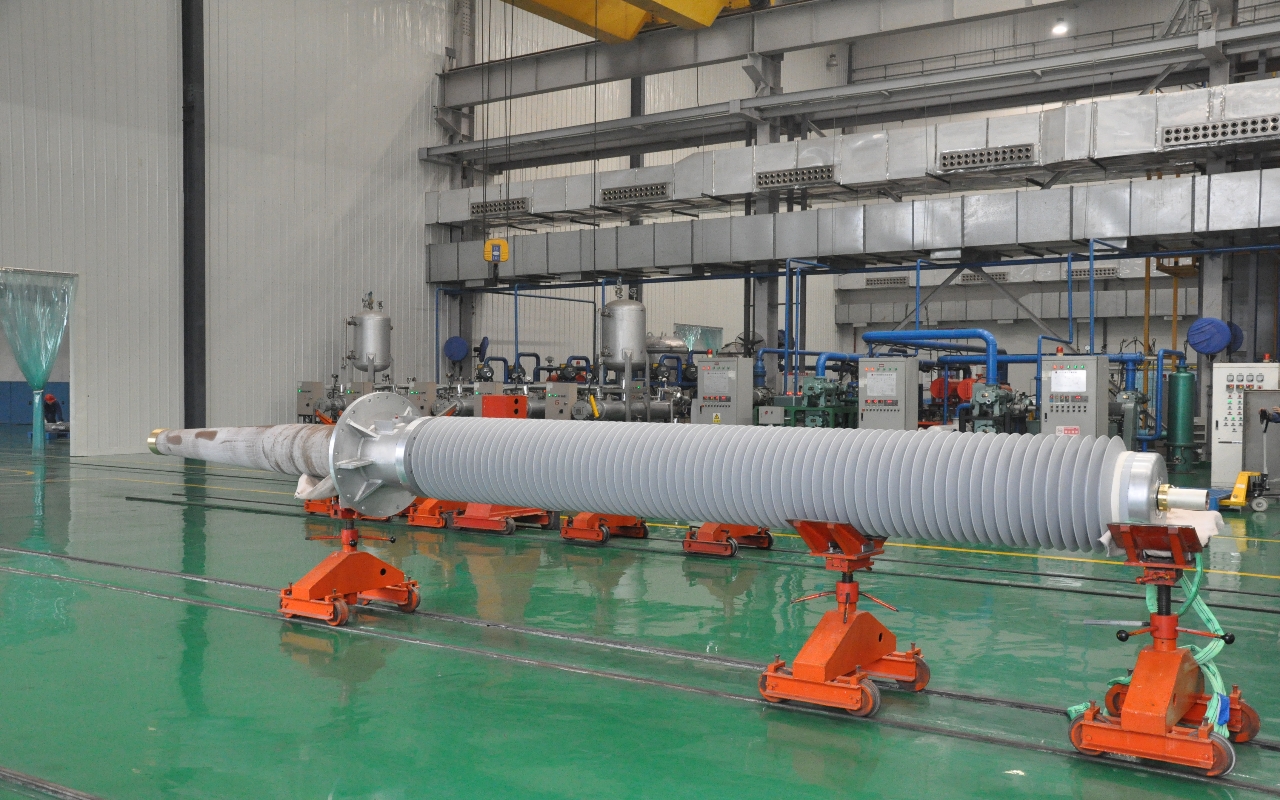
6-220kV oil-immersed HV transformer
Power transformer
Power transformer is a static electrical device used to convert a certain value of AC voltage (current) into another or several different values of voltage (current) with the same frequency.
A static device with two or more windings, in order to transmit electrical energy, converts the AC voltage and current of one system into the voltage and current of another system through electromagnetic induction at the same frequency. Usually, the values of these currents and voltages are different.
A transformer is a static electrical device used to transform AC voltage and current and transmit AC electrical energy. It achieves the transmission of electrical energy based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Transformers can be divided into power transformers, test transformers, instrument transformers, and special purpose transformers based on their uses: power transformers are necessary equipment for power transmission and distribution, as well as power user distribution; Equipment for conducting voltage withstand (boost) tests on electrical equipment using test transformers; Instrument transformers are used for electrical measurement and relay protection in distribution systems (PT, CT); Special purpose transformers include smelting furnace transformers, welding transformers, electrolytic rectifier transformers, small voltage regulating transformers, etc.
A power transformer is a static electrical device used to convert a certain value of AC voltage (current) into another or several different values of voltage (current) with the same frequency. When alternating current is applied to the primary winding, alternating magnetic flux is generated. The alternating magnetic flux is induced in the secondary winding through the magnetic conduction effect of the iron core, resulting in an alternating electromotive force. The height of the secondary induced electromotive force is related to the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings, that is, the voltage is directly proportional to the number of turns. The main function is to transmit electrical energy, therefore, rated capacity is its main parameter. Rated capacity is a commonly used value to represent power, which characterizes the size of transmitted electrical energy, expressed in kVA or MVA. When a rated voltage is applied to a transformer, it is used to determine the rated current that does not exceed the temperature rise limit under specified conditions. The most energy-efficient power transformer is the amorphous alloy iron core distribution transformer, which has the greatest advantage of having a particularly low no-load loss value. Whether the final no-load loss value can be ensured is the core issue to be considered throughout the entire design process. When arranging the product structure, in addition to considering that the amorphous alloy iron core itself is not subjected to external forces, it is also necessary to accurately and reasonably select the characteristic parameters of the amorphous alloy during calculation.
HEADING-TYPE-1
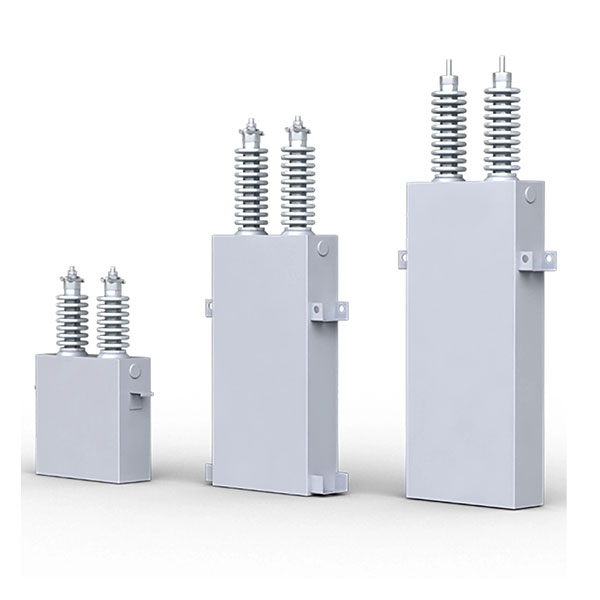
High voltage parallel capacitors are suitable for parallel connection in AC power systems with power frequency (50Hz or 60Hz) of 1kV and above. They are used to compensate for inductive reactive power, improve power factor, improve voltage quality, reduce line losses, and fully utilize the efficiency of power generation and supply equipment.
description2
HEADING-TYPE-1
High voltage parallel capacitors are suitable for parallel connection in AC power systems with power frequency (50Hz or 60Hz) of 1kV and above. They are used to compensate for inductive reactive power, improve power factor, improve voltage quality, reduce line losses, and fully utilize the efficiency of power generation and supply equipment.
description2